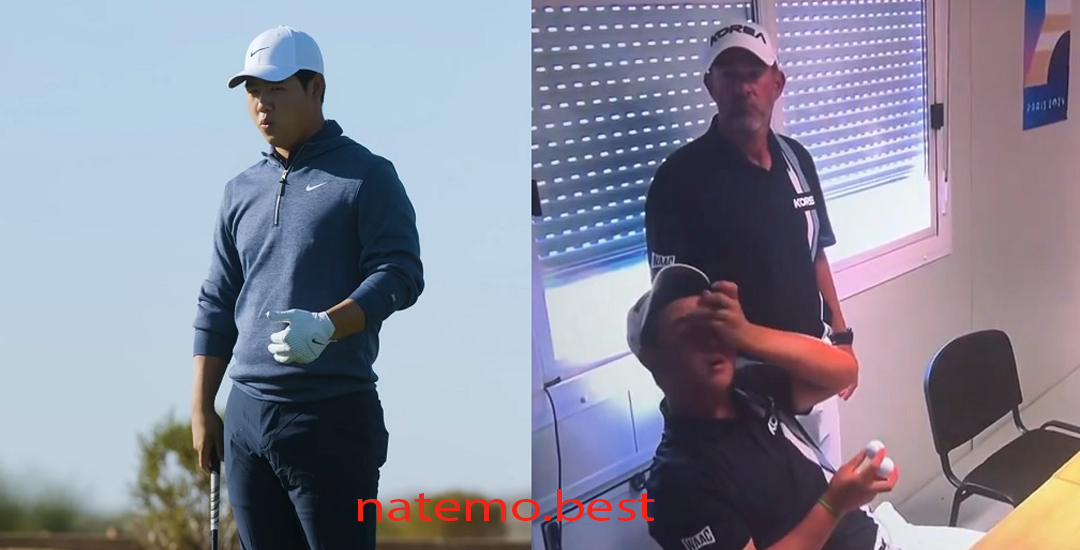
Pegolf Korea Selatan Tom Kim, Menangis Setelah Gagal Meraih Medali
Pendahuluan Pegolf Korea Selatan Tom Kim Dalam dunia olahraga, kisah-kisah penuh emosi sering kali menggambarkan…
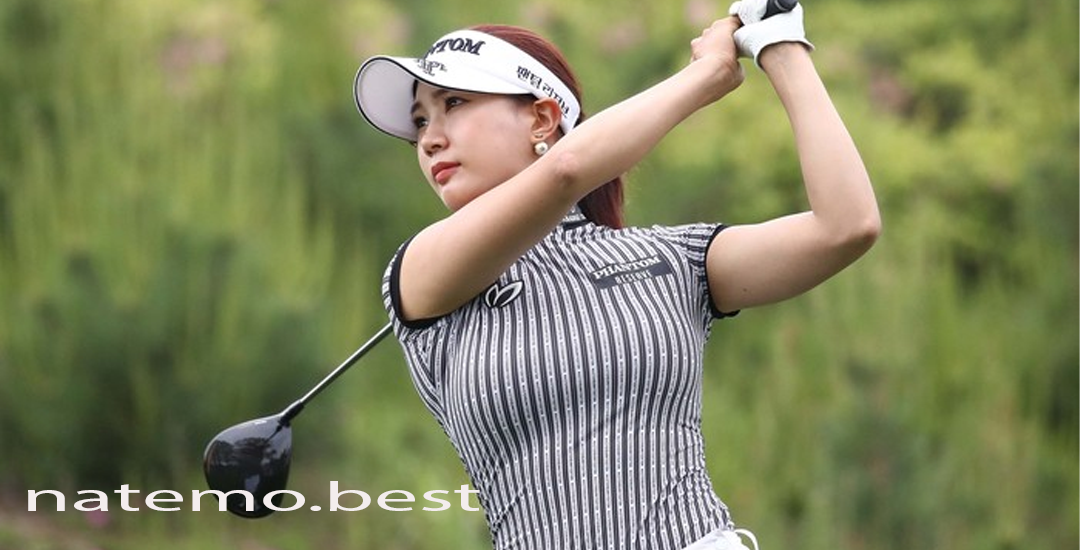
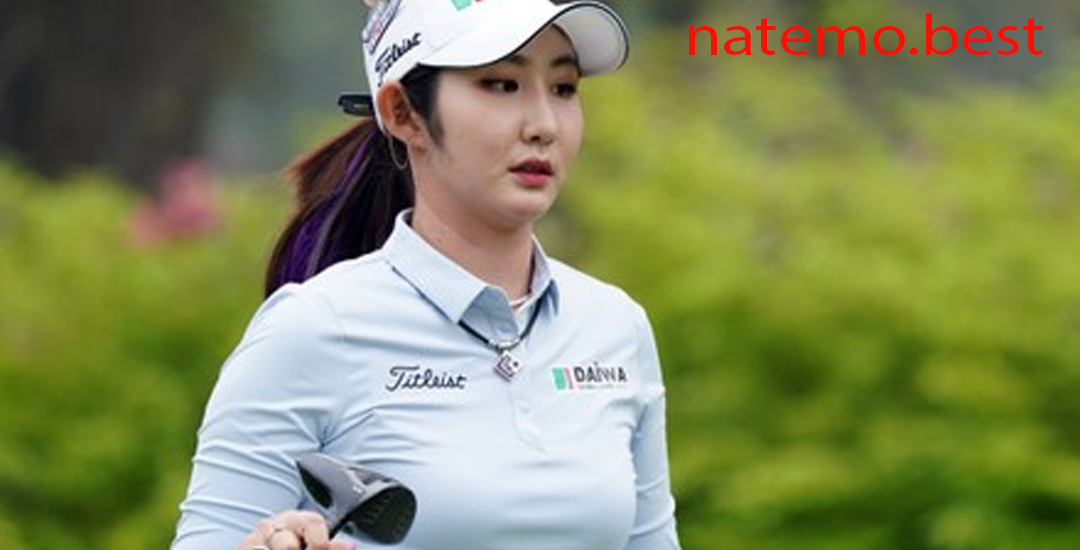
Meski Tampil di Luar Ruangan dan Bawah Terik Matahari, Pegolf Yoo Hyun-Ju Tetap Memperhatikan Penampilannya
Pendahuluan Meski Tampil di Luar Ruangan Dalam dunia olahraga golf, penampilan bukan hanya soal gaya,…
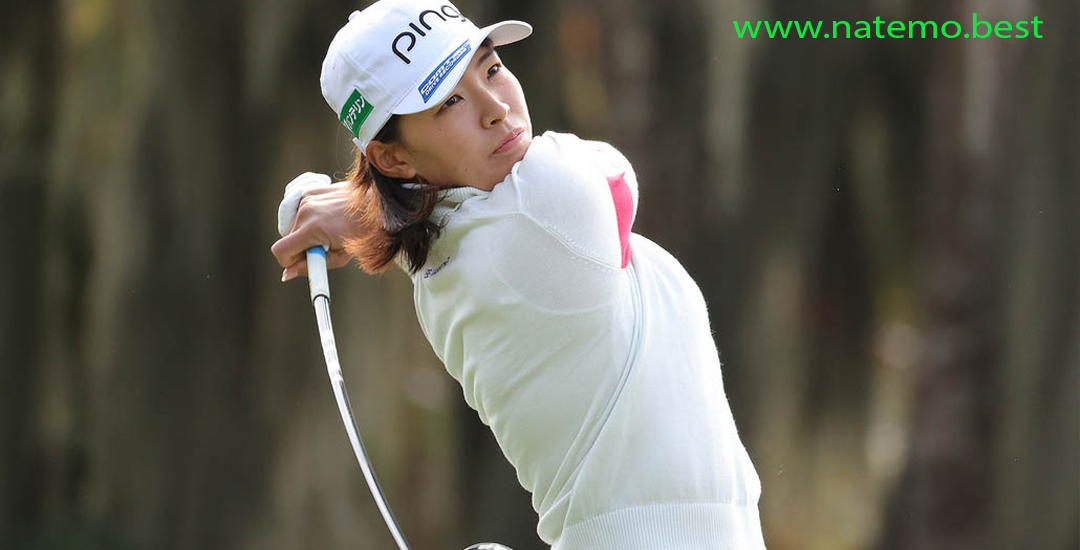
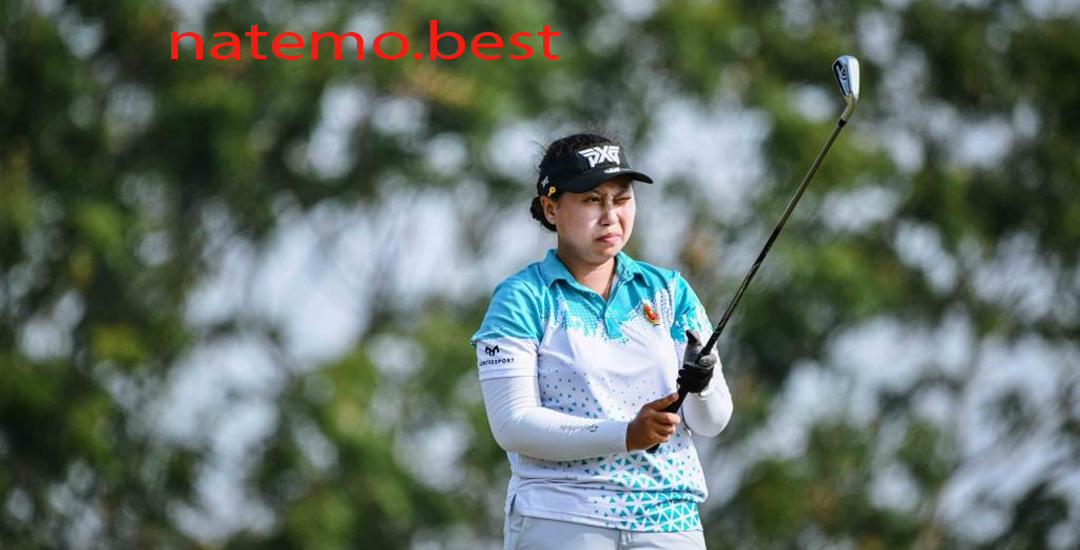
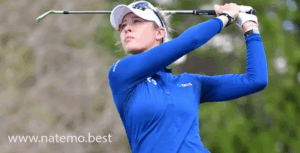
Seon Woo Bae: Perjalanan dan Prestasi Gemilang dari Yonsei University
Pendahuluan Seon Woo Bae adalah salah satu nama yang semakin bersinar di dunia golf profesional…
Kisah Perjuangan Alvi Novita: Atlet Golf Wanita Satu-Satunya di Jawa Timur
Pendahuluan Kisah Perjuangan Alvi Novita Dalam dunia olahraga, kisah perjuangan dan dedikasi para atlet seringkali…
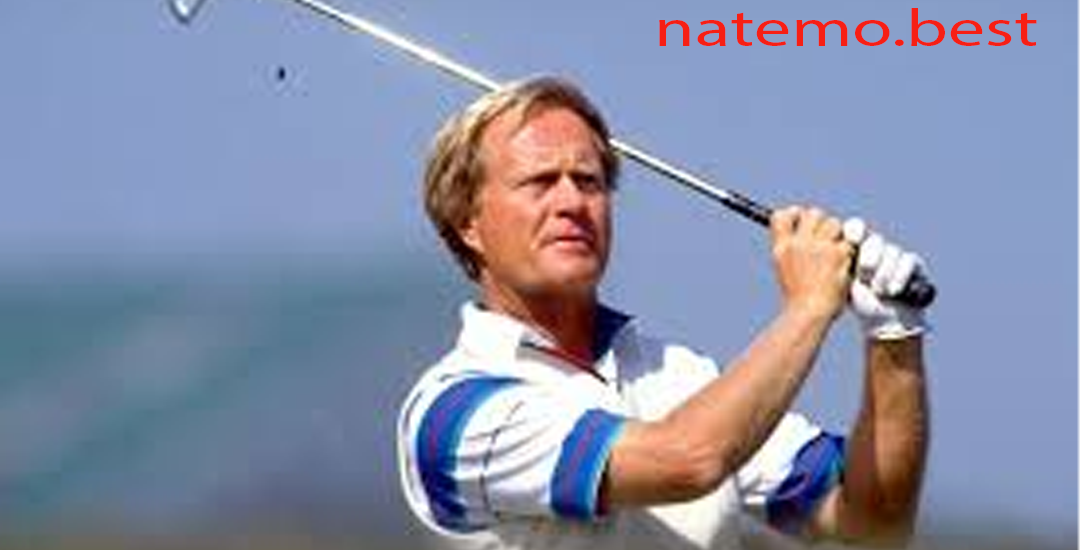
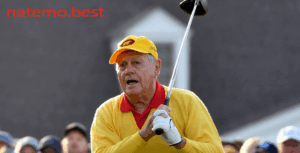
Jack Nicklaus: Legenda Golf yang Meraih Rekor Terbanyak dalam Koleksi Gelar Utama
Pendahuluan Jack Nicklaus Dalam dunia golf, nama Jack Nicklaus dikenal sebagai salah satu ikon terbesar…
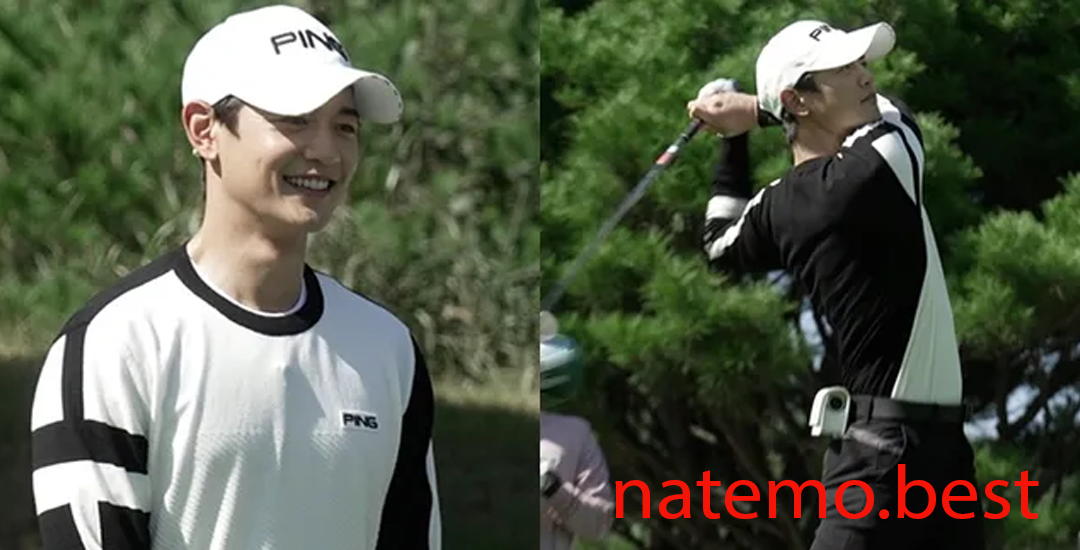
Pancarkan Pesona ‘Idol Atlet’: Minho SHINee Bergabung dalam Acara TV ‘Golf King’ Musim Kedua
Pendahuluan Pancarkan Pesona 'Idol Atlet Dalam dunia hiburan Korea Selatan, kombinasi antara bakat seni dan…
Format Permainan Golf: Memasukkan Bola Kecil Berwarna Putih ke Lubang di Golf Course
Pendahuluan Format Permainan Golf adalah salah satu olahraga rekreasi dan kompetitif yang populer di seluruh…
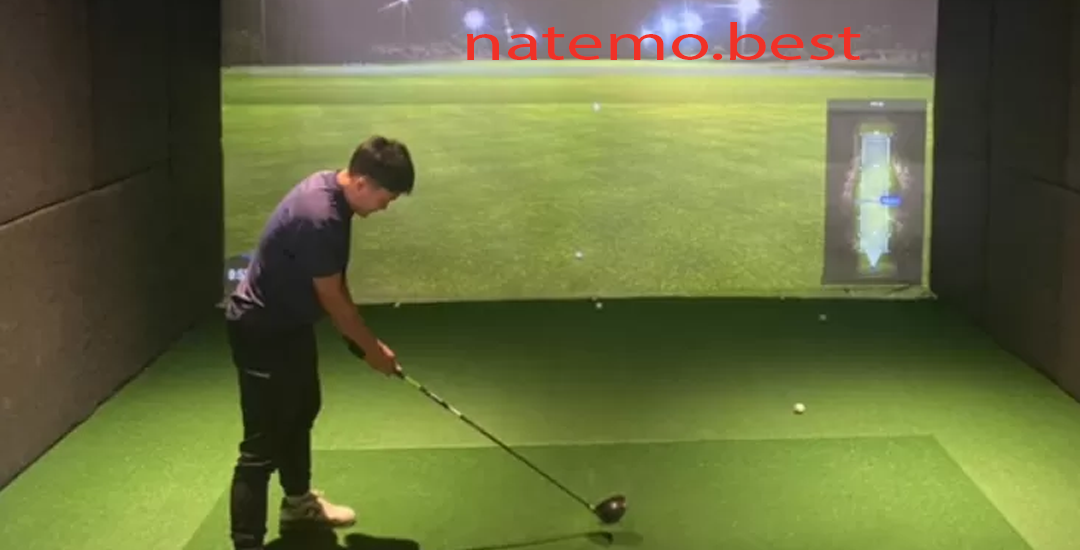
Mencoba Simulasi Bermain Gold Menggunakan Produk Terbaru dari BenQ: Pengalaman dan Review
Pendahuluan Mencoba Simulasi Bermain Gold Dalam era digital saat ini, permainan video semakin populer di…
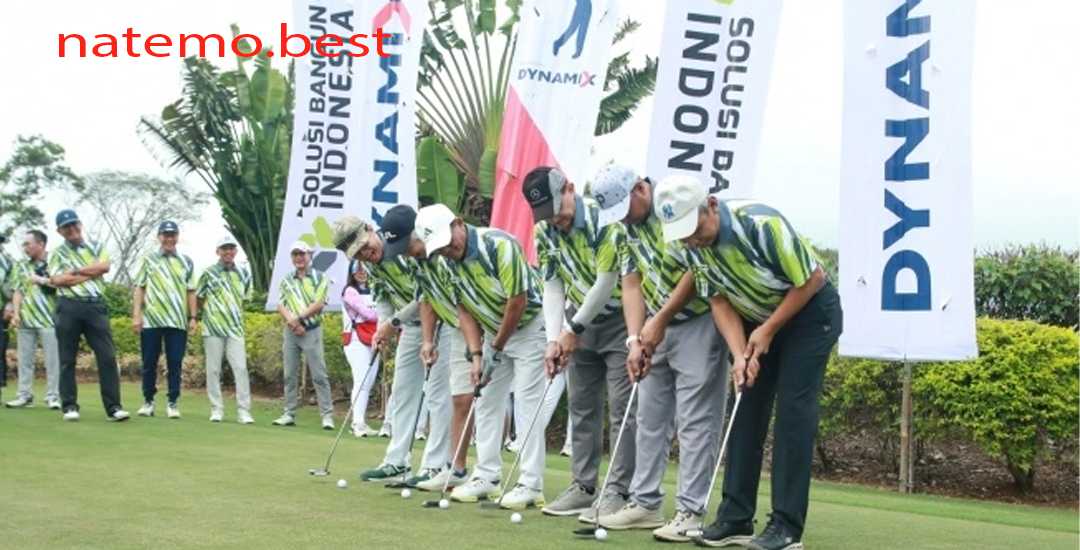
Turnamen Golf dengan Misi Sosial: Mendukung Pembangunan Fasilitas Pendidikan yang Layak
Pendahuluan Turnamen Golf dengan Misi Sosial Dalam era yang semakin peduli terhadap kesejahteraan masyarakat dan…
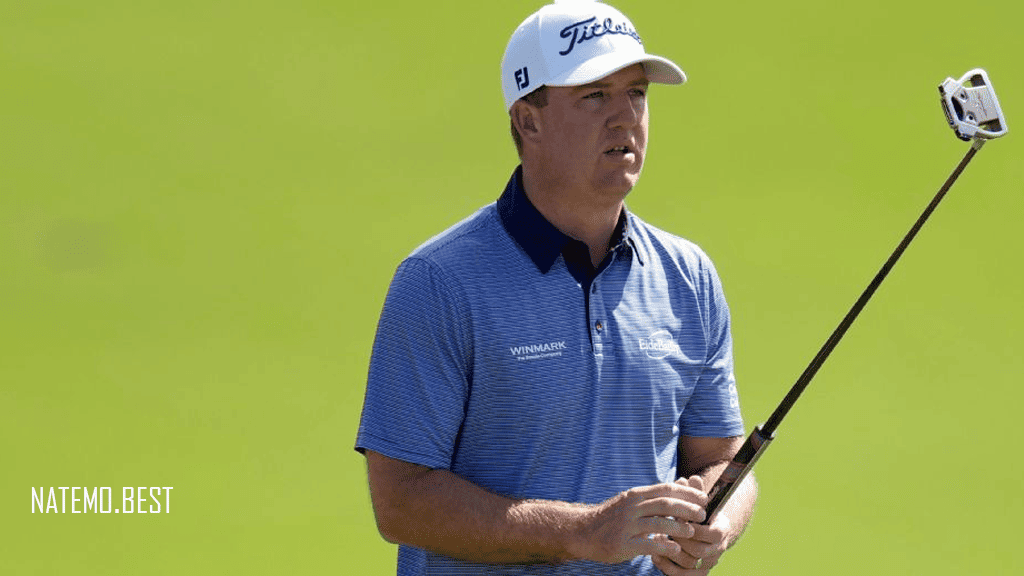
Tom Hoge: Profil dan Perjalanan Karier Profesional Golf
Pendahuluan Tom Hoge: Profil dan Perjalanan Karier Profesional Golf. Tom Hoge adalah seorang pegolf profesional…