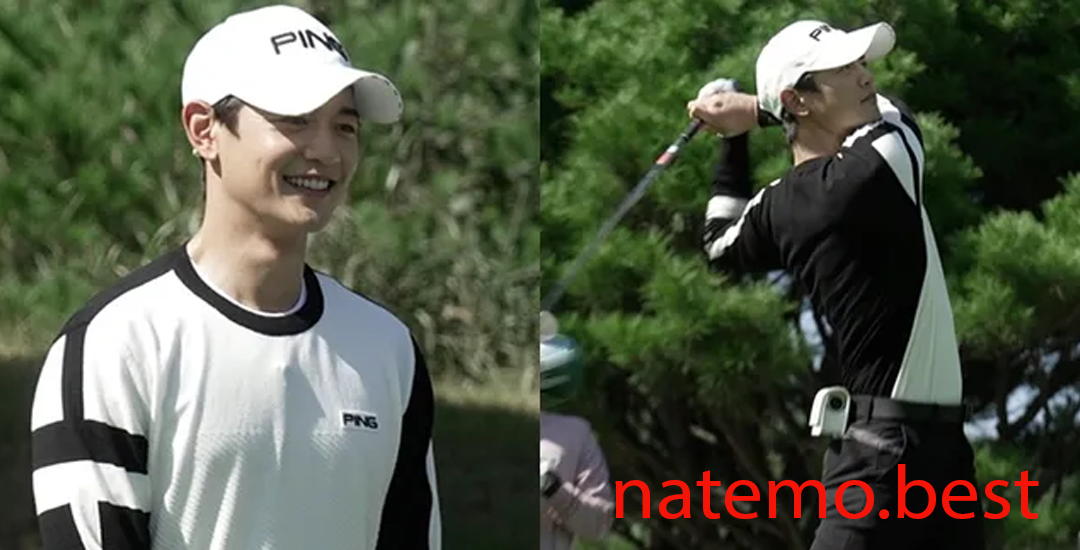
Pancarkan Pesona ‘Idol Atlet’: Minho SHINee Bergabung dalam Acara TV ‘Golf King’ Musim Kedua
Pendahuluan Pancarkan Pesona 'Idol Atlet Dalam dunia hiburan Korea Selatan, kombinasi antara bakat seni dan…
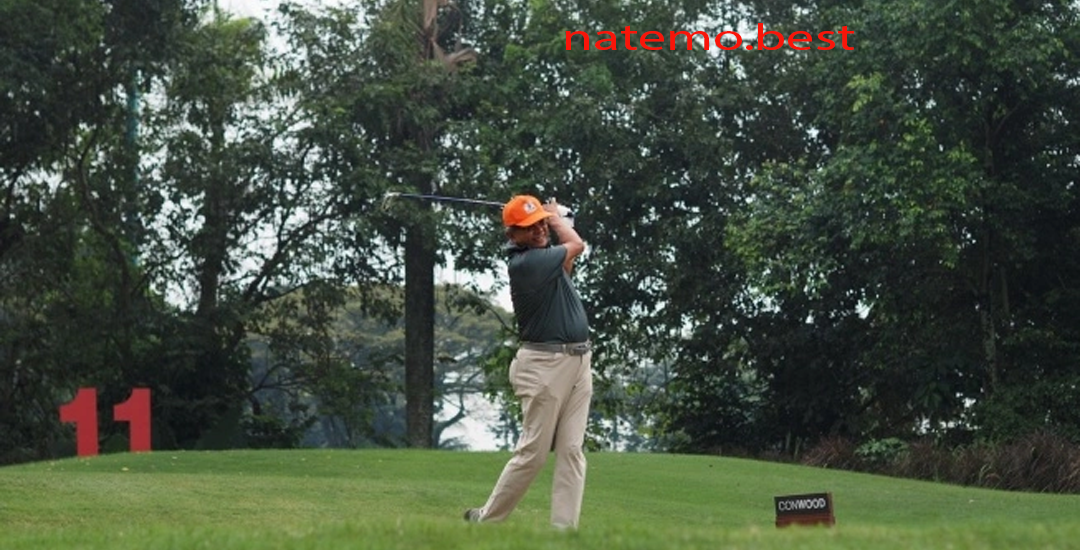
Format Permainan Golf: Memasukkan Bola Kecil Berwarna Putih ke Lubang di Golf Course
Pendahuluan Format Permainan Golf adalah salah satu olahraga rekreasi dan kompetitif yang populer di seluruh…
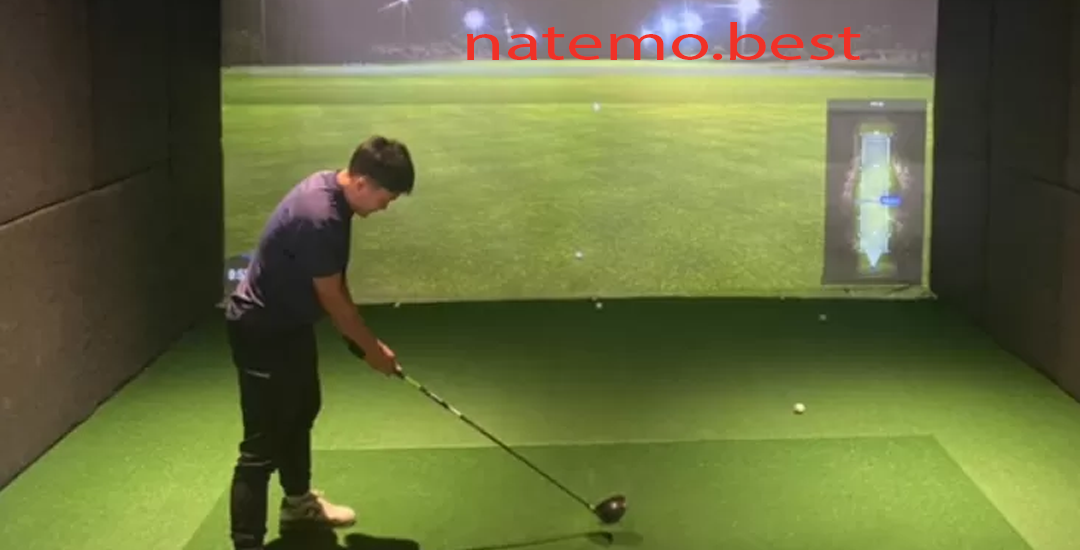
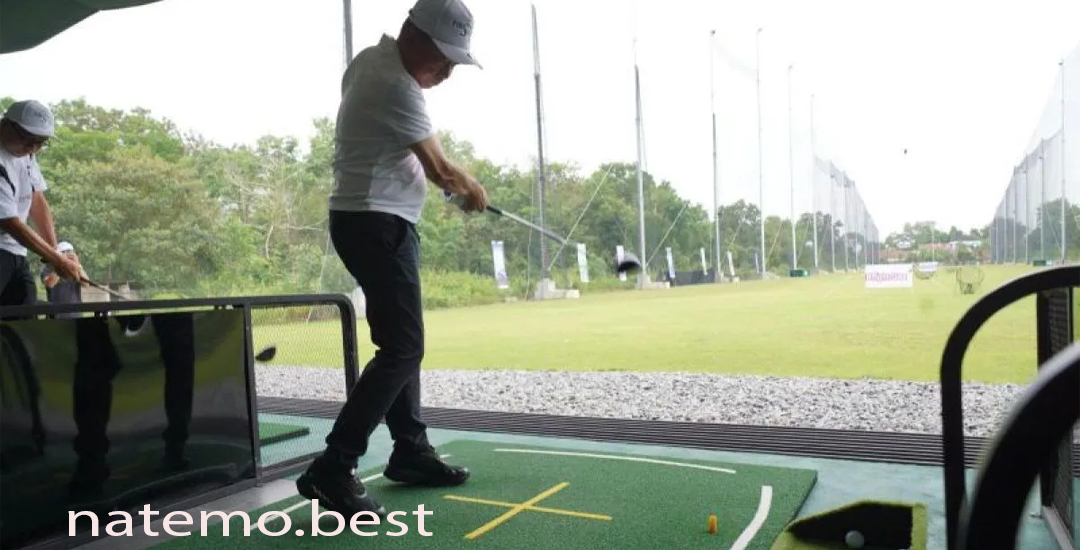
Mencoba Simulasi Bermain Gold Menggunakan Produk Terbaru dari BenQ: Pengalaman dan Review
Pendahuluan Mencoba Simulasi Bermain Gold Dalam era digital saat ini, permainan video semakin populer di…
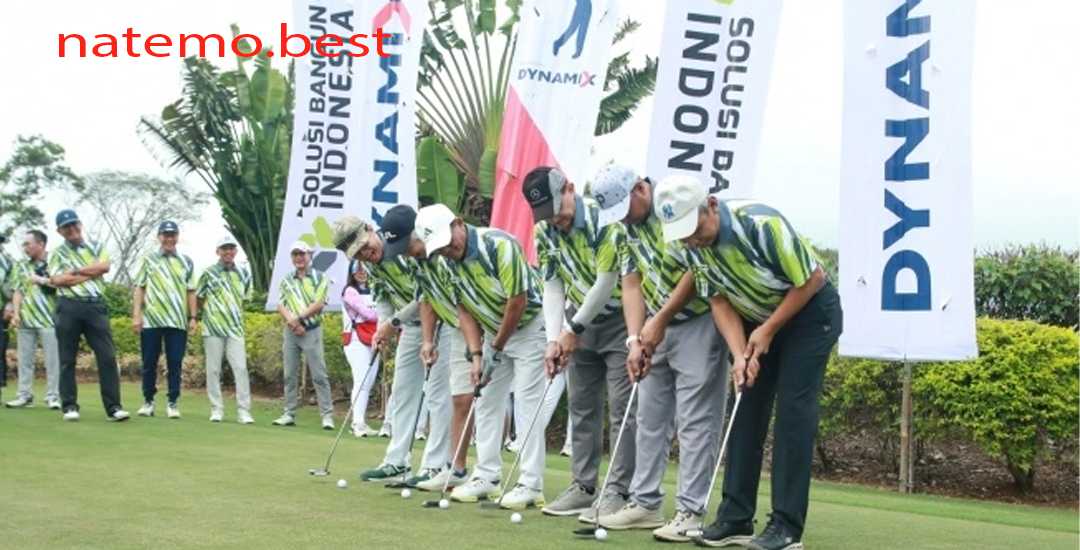
Turnamen Golf dengan Misi Sosial: Mendukung Pembangunan Fasilitas Pendidikan yang Layak
Pendahuluan Turnamen Golf dengan Misi Sosial Dalam era yang semakin peduli terhadap kesejahteraan masyarakat dan…
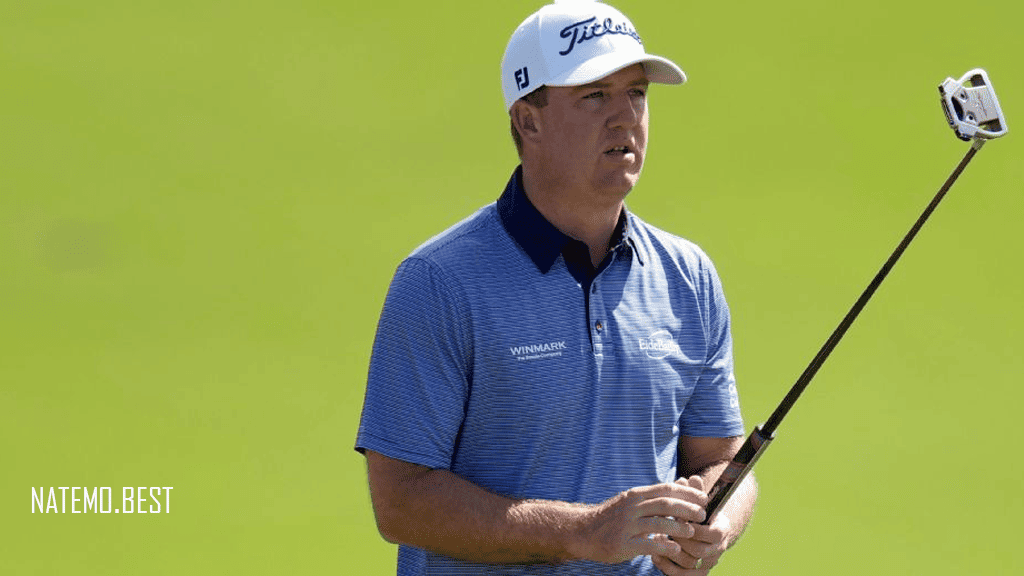
Tom Hoge: Profil dan Perjalanan Karier Profesional Golf
Pendahuluan Tom Hoge: Profil dan Perjalanan Karier Profesional Golf. Tom Hoge adalah seorang pegolf profesional…
Aldrich Potgieter Membuat Sejarah PGA Tour pada Usia 20 Tahun dengan Menang di Rocket Classic
Pendahuluan Aldrich Potgieter Pada usia yang masih sangat muda, Aldrich Potgieter berhasil mencuri perhatian dunia…
Wali Kota Pontianak Edi Rusdi Kamtono Menjajal Lapangan Golf First Wing Golf
Pendahuluan Wali Kota Pontianak, Edi Rusdi Kamtono, menghadiri acara peresmian lapangan golf terbaru di kota…
Membangun Fasilitas Pendidikan Lewat Turnamen Golf: Harmoni Olahraga dan Aksi Sosial
Pendahuluan Membangun Fasilitas Pendidikan Dalam era modern ini, olahraga telah menjadi sarana yang efektif tidak…
Kisah Inspiratif Atthaya Thitikul: Sang Golf Ace yang Berhasil Mengukir Sejarah di Panggung Dunia
Pendahuluan Kisah Inspiratif Atthaya Thitikul Dalam dunia olahraga golf, nama Atthaya Thitikul telah menjadi simbol…
Atthaya Thitikul Mengukir Prestasi Gemilang di Babak Final BMW Ladies Championship di Oak Valley Country Club
Pendahuluan Atthaya Thitikul Pada hari terakhir turnamen golf bergengsi BMW Ladies Championship yang digelar di…