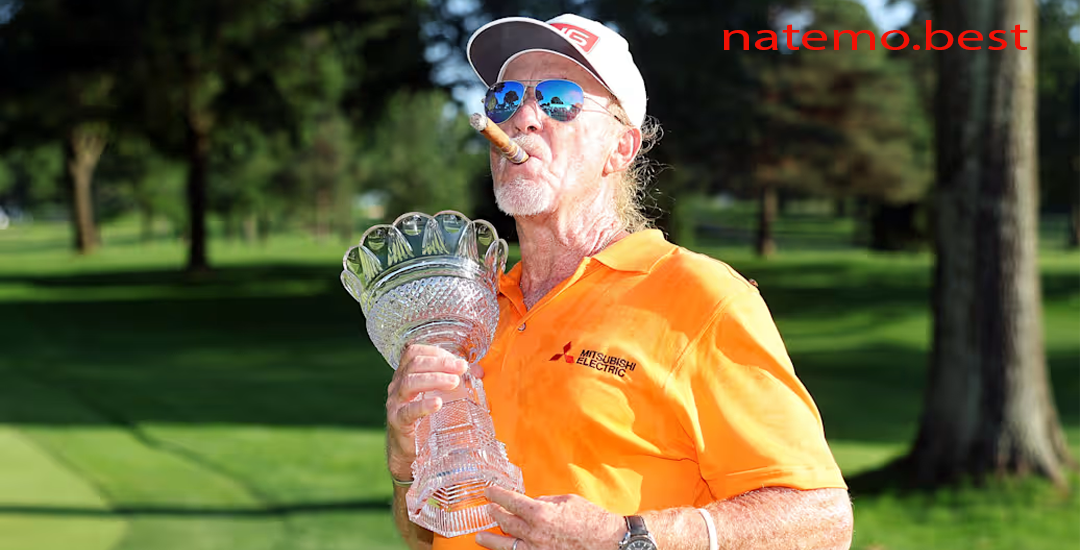
Miguel Angel Jiménez Buktikan bahwa Usia Hanyalah Angka dengan Kemenangan Dramatis
Pendahuluan Miguel Angel Jiménez Dalam dunia golf profesional, kisah inspiratif tentang pemain yang membuktikan bahwa…
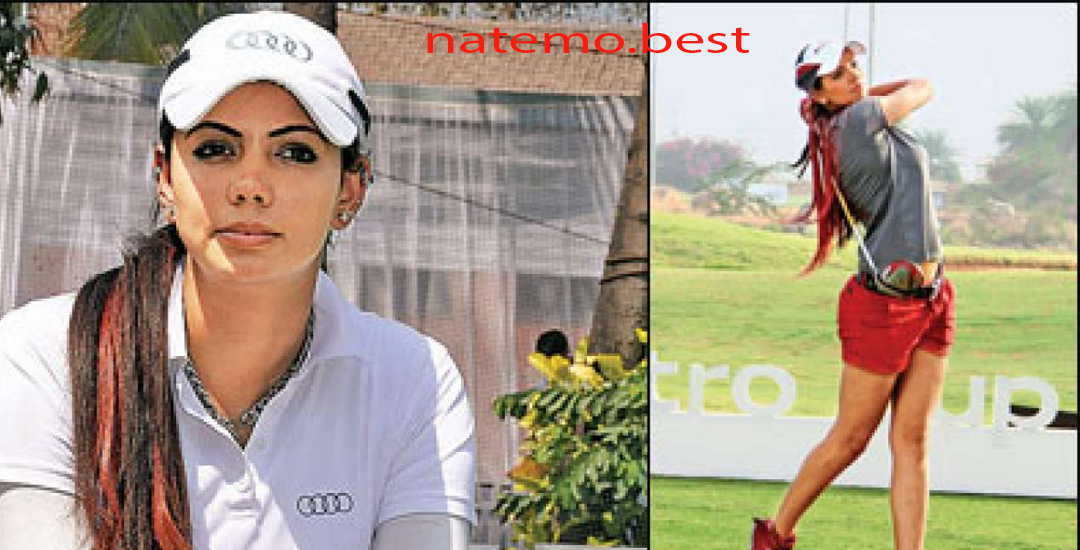
Sharmila Nicollet: Atlet Kebanggaan India yang Menginspirasi
Pendahuluan Sharmila Nicollet adalah salah satu atlet golf perempuan yang menjadi kebanggaan India. Dengan bakat…
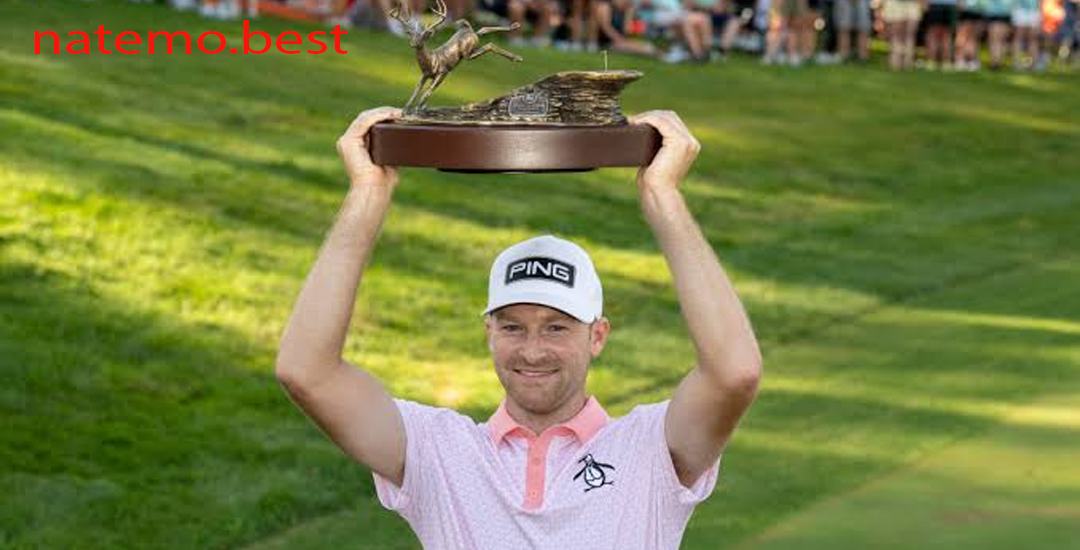
Brian Campbell Menangi John Deere Classic Via Babak Playoff
Pendahuluan Brian Campbell Menangi John Deere Classic Dalam sebuah pertandingan yang penuh ketegangan dan adu…
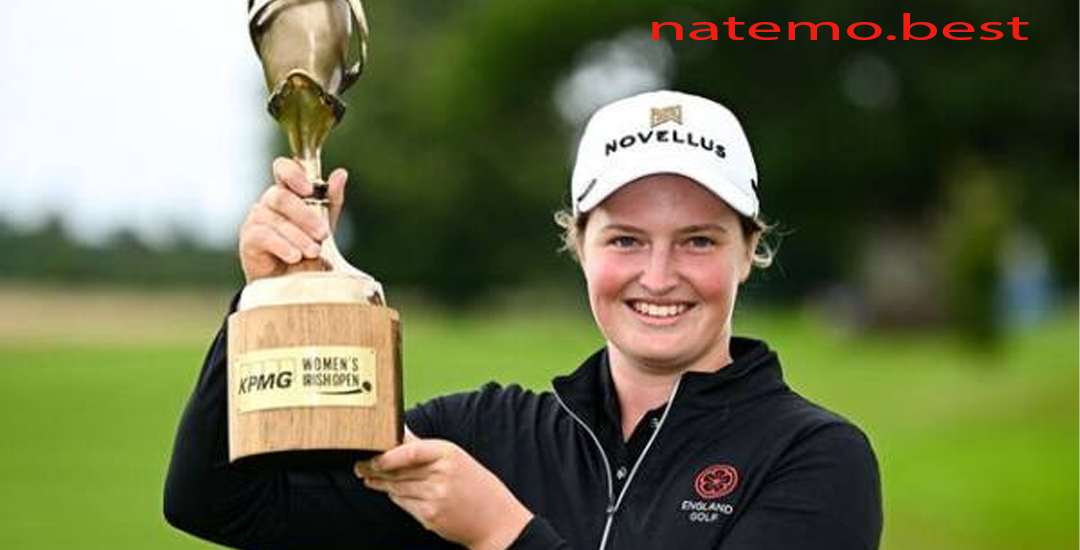
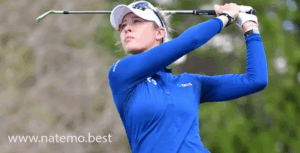
Lottie Woad: Pegolf Amatir Nomor Satu Dunia dengan Penampilan Dominan di Women’s Irish Open
Pendahuluan Lottie Woad Dalam dunia golf, kemenangan besar sering kali menjadi pencapaian yang dinantikan oleh…
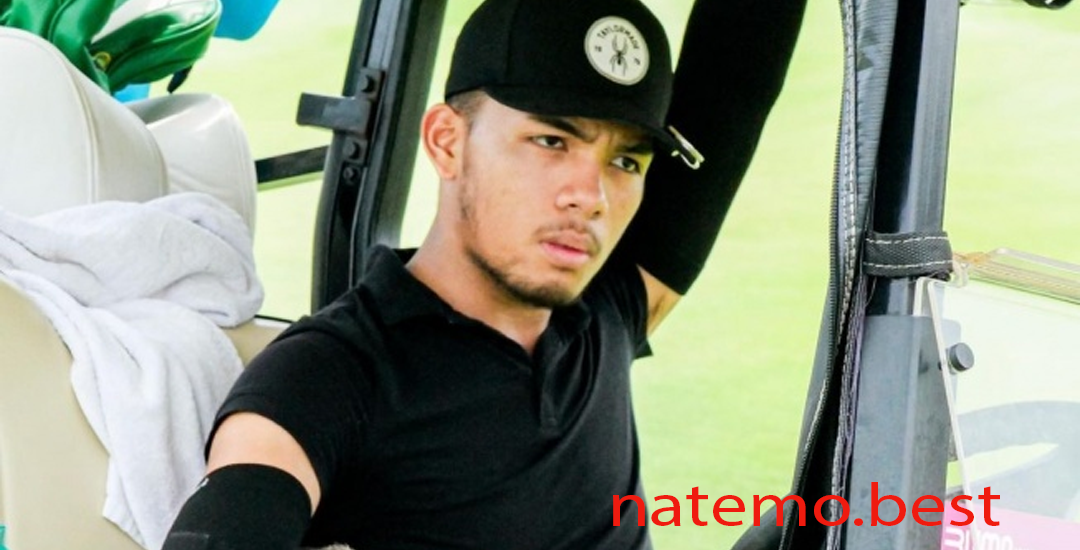
Saaih Halilintar: Dari Dunia Musik dan Konten ke Lapangan Golf Internasional
Pendahuluan Saaih Halilintar, dikenal sebagai anggota keluarga Gen Halilintar yang terkenal di media sosial dan…
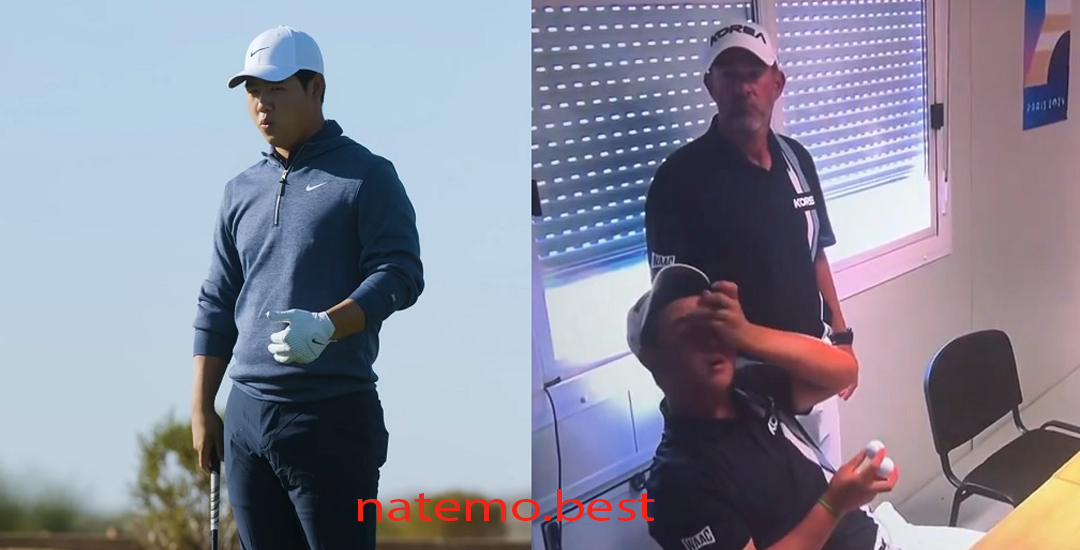
Pegolf Korea Selatan Tom Kim, Menangis Setelah Gagal Meraih Medali
Pendahuluan Pegolf Korea Selatan Tom Kim Dalam dunia olahraga, kisah-kisah penuh emosi sering kali menggambarkan…
Meski Tampil di Luar Ruangan dan Bawah Terik Matahari, Pegolf Yoo Hyun-Ju Tetap Memperhatikan Penampilannya
Pendahuluan Meski Tampil di Luar Ruangan Dalam dunia olahraga golf, penampilan bukan hanya soal gaya,…
Seon Woo Bae: Perjalanan dan Prestasi Gemilang dari Yonsei University
Pendahuluan Seon Woo Bae adalah salah satu nama yang semakin bersinar di dunia golf profesional…
Kisah Perjuangan Alvi Novita: Atlet Golf Wanita Satu-Satunya di Jawa Timur
Pendahuluan Kisah Perjuangan Alvi Novita Dalam dunia olahraga, kisah perjuangan dan dedikasi para atlet seringkali…
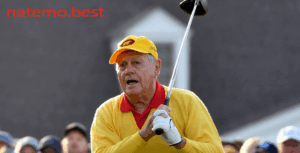
Jack Nicklaus: Legenda Golf yang Meraih Rekor Terbanyak dalam Koleksi Gelar Utama
Pendahuluan Jack Nicklaus Dalam dunia golf, nama Jack Nicklaus dikenal sebagai salah satu ikon terbesar…